Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR)
(heart-lung resuscitation) Pinch the person’s nose. Seal your mouth over their mouth and blow steadily and firmly into their mouth for about 1 second. Check that their chest rises. Give 2 rescue breaths. Continue with cycles of 30 chest compressions and 2 rescue breaths until they begin to recover or emergency help arrives.
First Aid Acronyms Explained – DRABC
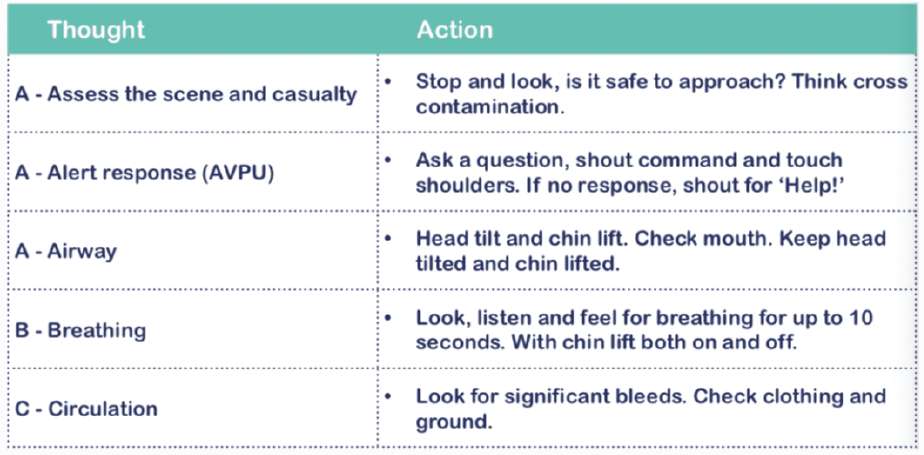
D – Danger
R – Response
A – Airway
B – Breathing
C – Circulation
The first aid acronym DRABC is a common acronym used by many first aid training organisations to help the first aider carry out a Primary Survey of a casualty in an emergency situation.
Danger – Is there any immediate danger? Assess the scene to make sure it is safe. If it is not safe, do not go any further, or make it safe before approaching the casualty.
Response – Is the casualty responsive? Ask them a loud question, squeeze their shoulders, Do they respond? If not shout for HELP!
Airway – Open the casualty’s airway by tilting the head back and lifting their chin.
Breathing – Check for 10 seconds to make sure the casualty is breathing. If they are not breathing effectively, call 999 and start CPR. If they are breathing move onto C for Circulation.
Circulation – This is a check for any significant blood loss. If you find bleeding, deal with it using the C.A.R.E. system
recovery position

Exhaust system usually has catalytic converter which reduces toxic and environment pollution by up to 90%.